Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes Mechanism
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes with Practice Problems. Nitrogen and sulfur nucleophiles will give S N 2 substitution in the case of 1º and 2º-halides.

Electrophilic Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Alkenes Youtube
Thus the carbonyl carbon and the three atoms attached to it lie in the same plane and the π-electron cloud is above and below this plane.

. The addition of pyridine to the mixture of alcohol and thionyl chloride results in the formation of alkyl halide with inverted configuration. Products 214 to 215. A recent application is the generation of highly reactive aryl radicals which are useful arylating reagents in synthesis by photoinduced electron transfer PET from photoredox catalysts to suitable precursors followed by bond scission 8 9However the choice of aryl radical precursors is currently limited to electron-poor arenes such as diazonium 6 10 or.
S N 1 S N 2 E1 or E2 the Largest Collection of Practice Problems. As shown in the following figure a hydrogen ion catalyzes the Markovnikovs addition. This concept of redox active ligands has resulted in new base metal catalysts for the asymmetric hydrogenation of alkenes as well as the hydrosilylation and hydroboration of olefins.
HBr and HCl to form alkyl halides. Mechanism The mechanism of the reaction involves the following three steps. The addition of hydrogen bromide to 1butyne gives 2bromo1butene as the major product of the first step.
Which of the following options correctly describe the mechanism of acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene. The energy behavior is shown in Figures 5A and 5B for the two selected alkenes. The reaction intermediate is an epoxide.
Preparation of Hydrocarbons Alkenes. Addition Reactions of Alkenes. Electrophilic addition to conjugated dienes occurs through 12 and 14-addition mechanism out of Q.
In addition to primary amines secondary amines led to reductive coupling with nitriles and provided tertiary chiral amines in up to 85 yields and 99 ee Fig. In high dielectric ionizing solvents S N 1 and E1 products may be formed. The elements of water can be added to the doublebonded carbons of an alkene in either a Markovnikovs or an antiMarkovnikovs manner.
Substituted benzene rings may also be deduced in this fashion and hydroxy. Most of the reactions involving the preparation of alkenes involve elimination process. The antiMarkovnikovs addition results from a hydroborationoxidation reaction.
There are 3 mechanisms suggested for the elimination reactions. Because the hydrogen is absorbed on the catalyst surface. If the two carbon atoms at the double bond are linked to a different number of hydrogen atoms the halogen is found preferentially at the carbon with fewer hydrogen.
Benzyl C 6 H 5 CH 2. C n H 2n. Mechanism of Dehydration of Alcohols.
With acrylamide the reaction barrier of the second mechanism was found to be 145 eV which is 03 eV lower than the barrier 171 eV for methacrylamide. Download high-res image 850KB Download. From alkenes i By acid catalysed hydration.
Oxidative addition of aryl and alkyl halides to a reduced iron pincer complex. In case of unsymmetrical alkenes the addition reaction takes place in accordance with Markovnikovs rule Unit 13 Class XI. Formation of alkenes.
All these eliminations are β- eliminations. H2O acts as a nucleophile in this reaction. Hydrogen halides react with alkynes in the same manner as they do with alkenes.
Evidence for this mechanism is as follows. Alcohol dehydration is an example of an elimination reaction which is quite the opposite of substitution reaction and addition reaction. Alkenes react with water in the presence of acid as catalyst to form alcohols.
In addition the oxygen atom also has two non bonding electron pairs. Hydrohalogenation is the addition of hydrogen halides such as HCl or HI to alkenes to yield the corresponding haloalkanes. The product is cyclohexane and the heat of reaction provides evidence of benzenes thermodynamic stability.
The first step involves addition of H to the CC double. 1212 Structure of the Carbonyl. CH 3 CHCH 2 HI CH 3 CHICH 2 H.
Secondary alcohols get oxidized to ketones and primary are oxidized to carboxylic acids by chromic acid. The Role of the Solvent in S N 1 S N 2 E1 and E2 Reactions. Inversion results because the pyridine reacts with ROSOCl to give ROSONC 5 H 5 before anything further can take place.
S N 1 S N 2 E1 E2 How to Choose the Mechanism. Water hydrolysis will be favorable for 2º 3º-halides. Delydrobalogenation of vinyi halides is essentially.
Addition Although it does so less readily than simple alkenes or dienes benzene adds hydrogen at high pressure in the presence of Pt Pd or Ni catalysts. The second step involves addition of an OH- to a carbocation. Select all that apply.
Notably for products 210 and 214 12 to 14 racemization is observed which can be explained by the comparably high acidity of the α-hydrogen atom in the. Markovnikovs Rule with Practice Problems. The mechanism of alkyne hydrogenation is identical to that of the alkenes.
3º-halides will probably give E2 elimination with nitrogen nucleophiles they are bases. The bond angles are approximately 120 as expected of a trigonal coplanar structure Figure 121.
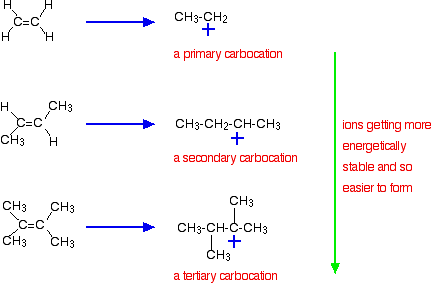
9 2 Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Symmetrical Alkenes Chemistry Libretexts
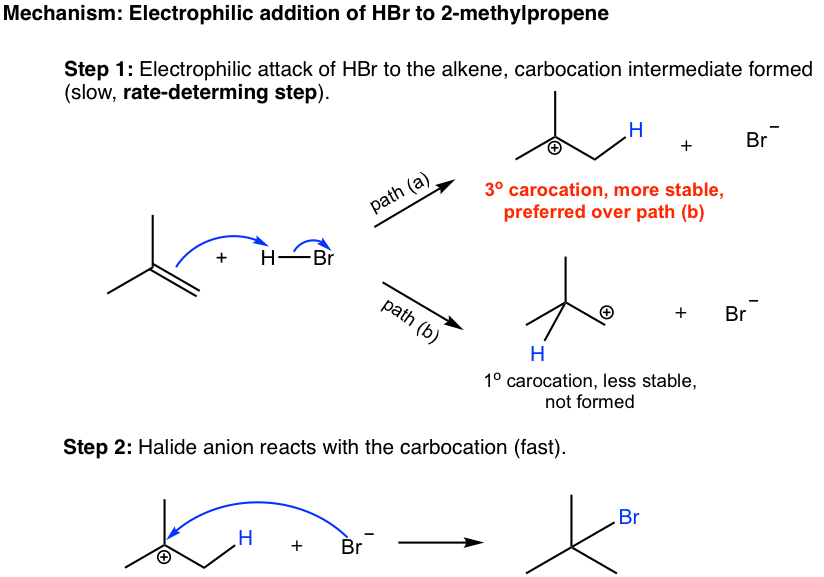
10 2 Reactions Of Alkenes Addition Of Hydrogen Halide To Alkenes Organic Chemistry I
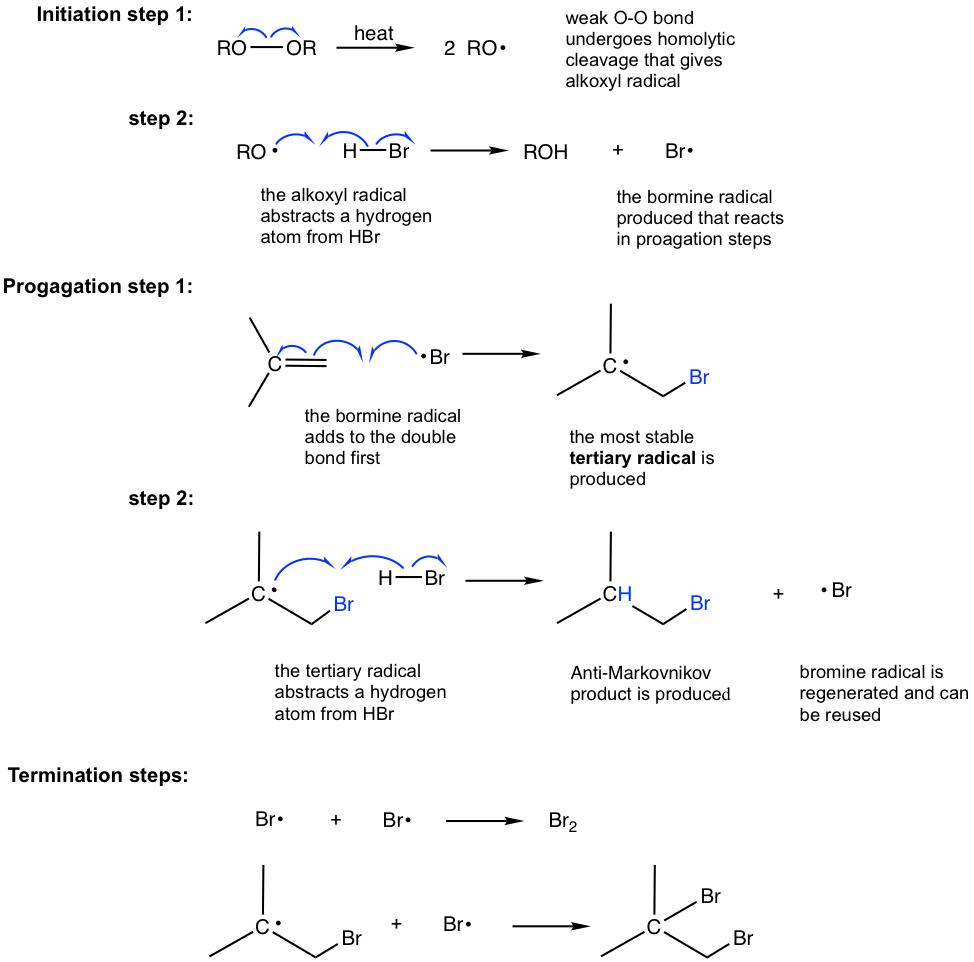
10 2 Reactions Of Alkenes Addition Of Hydrogen Halide To Alkenes Organic Chemistry I

Electrophilic Addition Reactions Of Alkenes Mcc Organic Chemistry
Comments
Post a Comment